RFID Technology
Welcome to the user guide to RFID Technology. In this tutorial we have to discuss Different types of RFID, how to use, how to interface with the microcontroller.
RFID stands for Radio Frequency Identification. It is one of the wireless technology/ Wireless Radiofrequency for noncontact data access applications.
How RFID Works
RFID communication has a transmitter unit and a Receiver unit.
NOTE: Transmitter unit also called as RFID card/tag. Receiver unit also called as RFID Reader
Transmitter unit or also we can be called as RFID Tags. It has some security id numbers, this id number is not unique it will different for every RFID tag/card, so each and every RFID card has its own ID number. When you put the RFID card into the RFID reader field area then the RFID card ID number will access by the RFID reader, the distance between the RFID card and RFID reader will depend on the active or passive type of the RFID card.
RFID tags are classified into active RFID cards and passive RFID cards.
Receiver unit or also called RFID Reader
Applications of RFID:
- Personal ID cards
- Library Books
- NFC Applications
- Access control
- Pharmaceuticals
Types of RFID:
RFID Technology is classified based on Frequency ranges, such as
Low Frequency(LF): 30Khz to 300Khz
High Frequency(HF): 3Mhz to 30Mhz
Ultra High Frequency(ULF): 300Mhz to 3Ghz
Passive and Active RFID Tags
Active:
This is related to Ultra High Frequency, which means they are operated with long-range wireless communication. RFID Tags have their own in-built Power supply in Transmitter Tags, because of this extra power source transmitter and receiver communicate up to 100mt distance is the long-range for RFID Communication. Usually, Active RFID tags a little bit costly and larger compared to passive RFID tags.
Applications of Active-RFID Tags
- Military applications
- Asset management
- Products tracking
- Security scanning
Passive:
This is the Short-range of RFID communication. Passive tags have no internal power source, so the RFID tags are activated by only Radio waves from the RFID Reader module, so these passive cards work up
to short ranges only (10cm to 100cm).Based on this requirement passive RFID cards are less weight and low cost.
Applications of Passive-RFID Tags
- Personal ID cards
- Students ID management system.
- Low-security access control
How to implement RFID Technology | How to interface RFID with ARDUINO
In this session, we have to discuss how to access the ID number from the RFID cards/Tags. For this purpose definitely, you need to interface with Microcontroller, here we are using an ARDUINO controller.
NOTE: RFID the interface works with Serial communication (UART) protocol.
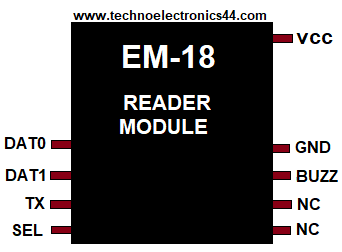
Hardware Interface:
RFID Reader has power supply pins, data pins.
Power supply pins: 5v, GND
Data pins: Tx, Rx
 |
| RFID Arduino |
 |
| EM18-RFID READER ARDUINO |
CODE:




0 Comments