Pin Out:
|
PIN |
DESCRIPTION |
|
VCC |
Power ( + Terminal ) |
|
GND /VSS |
Ground (- Terminal) |
|
U/D |
Up/Down |
|
INC |
Increment |
|
CS |
Chip select |
|
VH/RH |
High potential
terminal |
|
VW/RW |
Optimum potential |
|
VL/RL |
Low potential |
Features
Ø Solid-state potentiometer
Ø 99 resistive elements.
Ø Three-wire Serial interface
Ø 100 wiper tap points
Ø Low power CMOS technology
Ø Standby current (750uA)
Ø Active current (3A-max)
Specifications
Ø Supply voltage: 3V-5V
Ø Chip: X9C103S
Ø Dimensions : 28 x 14 x 4 (LxWxH) mm.
Ø 10K span potentiometer.
Ø Potentiometer center tap between 0-10k slide in total 100 (potentiometer wiper typical impedance 40 ohms)
Ø VL and VH Digital Potentiometer sliding rheostat port corresponding to the low-end and high-end, allowing the input voltage range -5V to + 5V.
Standard Resistance Value:
Ø X9C102 = 1kW
Ø X9C103 = 10kW
Ø X9C503 = 50kW
Ø X9C104 = 100kW
How to use X9C103S-DIGIPOT
Vcc, Gnd are power supply pins connected to the dc power source (required voltage), U/D, INC, CS are input pins with the active LOW state, remaining three pins VH/RH, VW/RW, VL/RL are output pins, so this output terminal acts just like a present(Potentiometer) three terminals.
Principles of operation
Instructions and programming
The INC,
U/D and CS inputs control the development of the wiper along with the resistor
exhibit. With CS set LOW, the gadget is chosen and empowered to react to the
U/D and INC inputs. HIGH to LOW changes on INC will addition or decrement
(contingent upon the condition of the U/D information) a 7-piece counter.
The yield of this counter is
decoded to choose one of 100 wiper positions along with the resistive cluster. The
estimation of the counter is put away in non-unstable memory at whatever point
CS changes HIGH while the INC input is additionally HIGH. The framework may
choose the X9Cxxx, move the wiper and deselect the gadget without putting away
the most recent wiper position in non-unstable memory.
After the wiper development is preceded
as recently depicted and once the new position is reached, the framework should
keep INC LOW while taking CS HIGH. The new wiper position will be kept up until
changed by the framework or until a shut down/upcycle reviewed the recently
put away information. This technique permits the framework to consistently
control up to a pre-set worth put away in non-unpredictable memory; at that point
during framework activity, minor changes could be made. The changes may be
founded on client inclination, i.e.: framework boundary changes because of
temperature float, and so forth The territory of U/D might be changed while CS
stays LOW. This permits the host framework to empower the gadget and afterward
move the wiper all over until the appropriate trim is achieved.
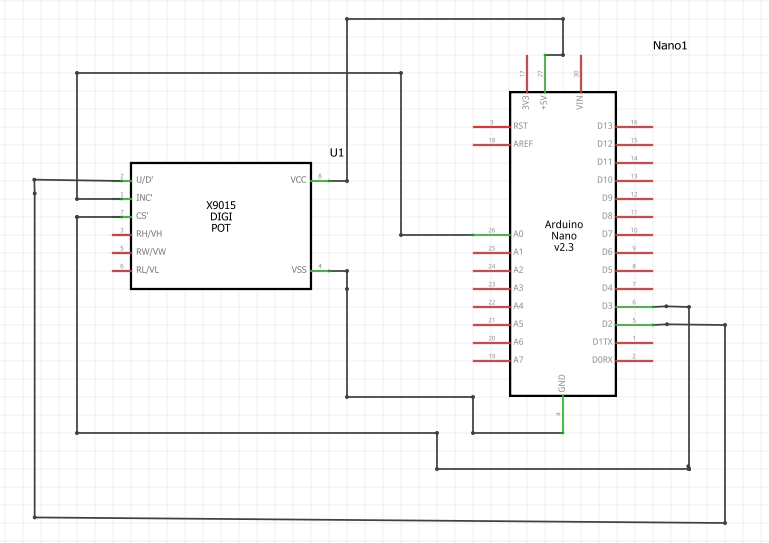
Arduino with X9C103S-DIGIPOT
Schematic of DIGI-POT
DATASHEET
Applications
- sensors trimming
- calibration of readings
- instrumentation-gain or offset adjustment
- optical networks
- audio controllers






0 Comments